SEO Blog
How Long Until a Tooth Infection Kills You? Understanding the Risks, Symptoms, and Treatment
How Long Until a Tooth Infection Kills You? Understanding the Risks, Symptoms, and Treatment
Tooth infections, if left untreated, can become life-threatening. The question, “How long until a tooth infection kills you?” is alarming but crucial. Many people underestimate the dangers of a tooth infection, assuming it’s just a localized problem affecting their teeth. In reality, infections that begin in a tooth can spread throughout the body and potentially lead to serious complications, including death. This article explores how long it can take for a tooth infection to become fatal, the progression of the infection, and the steps to prevent it from getting worse.
What Is a Tooth Infection?
A tooth infection, also known as a tooth abscess, is a pocket of pus caused by a bacterial infection in or around the root of a tooth. It typically develops when bacteria invade the tooth through cavities, cracks, or gum disease. The infection can spread beyond the tooth itself and affect other areas of the body if left untreated. While tooth infections are generally treatable, delaying care can result in severe dental infection complications.
Causes of a Tooth Infection
- Tooth decay: Cavities that go untreated allow bacteria to penetrate the deeper layers of the tooth, leading to infection.
- Gum disease: Advanced gum disease (periodontitis) can cause the gums to recede, exposing the roots of the teeth and making them more susceptible to infection.
- Cracked or chipped teeth: Breaks in the enamel provide entry points for bacteria.
- Dental procedures: Certain dental implants or surgeries, if not performed correctly, can introduce bacteria into the body.

Symptoms of a Tooth Infection
Early detection of dangerous tooth infection symptoms is crucial for effective treatment. Signs of a severe dental infection include:
- Pain: A sharp, throbbing pain near the infected tooth or in the surrounding gum tissue.
- Swelling: Localized swelling in the face or gums that can spread to other areas, such as the neck.
- Fever: An elevated temperature may indicate the infection is spreading.
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing: This occurs when swelling spreads to the throat, making it hard to breathe or swallow.
- Foul taste or smell: If the abscess ruptures, pus can leak into your mouth, causing an unpleasant taste or smell.
- Swollen lymph nodes: These are signs that the body is trying to fight off the infection.
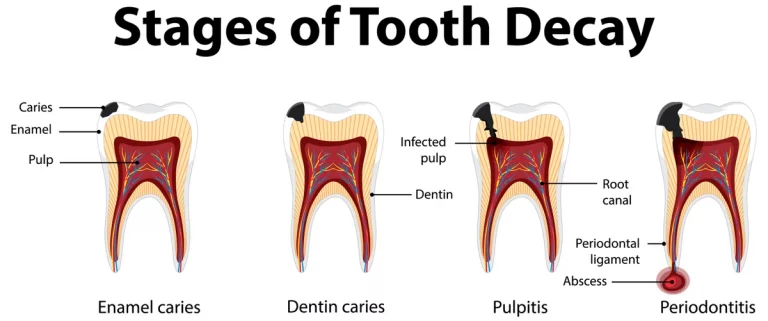
Progression of a Tooth Infection: Timeline and Stages
Understanding the tooth infection timeline is key to knowing how long it can take for the infection to escalate to a dangerous level. Tooth infections progress through several stages, each of which has increasing risks.
Stage 1: Initial Infection
In the beginning, the infection is confined to the tooth and gum area. Pain, sensitivity, and swelling are the first signs. At this stage, the infection can be treated relatively easily with antibiotics or a root canal.
Stage 2: Abscess Formation
As the infection worsens, a tooth abscess forms. This is a collection of pus that causes intense pain and pressure. If left untreated, the abscess can burst, allowing the infection to spread through the body.
Stage 3: Infection Spread
When the infection is not treated, it can spread to surrounding tissues, including the jaw, neck, and head. In more severe cases, the bacteria can enter the bloodstream, leading to sepsis, a potentially life-threatening condition.
How Long Until a Tooth Infection Kills You?
The timeline for how long it takes for a tooth infection to become life-threatening varies based on factors like the patient’s overall health, the severity of the infection, and how quickly it spreads.
- Within weeks or months: In most cases, a tooth infection progresses gradually. Left untreated, a tooth abscess could lead to life-threatening complications within weeks to months.
- Soon or in one to three days: If the infection spreads rapidly into the bloodstream or vital organs, it could become fatal in just one to three days.
- Several months to years: In some cases, an untreated infection may persist for several months, causing chronic pain and swelling but eventually resulting in severe complications if not addressed.
Complications from Untreated Tooth Infections
Untreated tooth abscesses carry significant risks. The infection can spread to other parts of the body, causing life-threatening conditions.
Sepsis
Sepsis occurs when the infection spreads into the bloodstream. It can cause organ failure and death if not treated promptly. Sepsis is one of the most severe dental infection death risks.
Brain Abscess
If the infection spreads to the brain, it can cause a brain abscess, a potentially fatal condition. Symptoms include severe headaches, fever, and confusion. This is a rare but deadly complication of an untreated tooth infection.
Ludwig’s Angina
This is a serious form of cellulitis (a bacterial skin infection) that occurs in the floor of the mouth under the tongue. It can obstruct the airway, making it difficult to breathe. Immediate treatment is required to prevent suffocation.
Prevention and Treatment of Severe Dental Infections
Preventing a tooth infection from escalating is the best way to avoid life-threatening complications. Regular visits to the dentist, good oral hygiene, and prompt treatment of any dental issues can reduce the risk of developing a tooth abscess.
Preventing Tooth Infections
- Maintain oral hygiene: Brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and using mouthwash can help prevent infections.
- Regular dental check-ups: Visiting your dentist every six months for cleanings and exams can catch problems before they worsen.
- Address dental issues immediately: If you experience tooth pain, swelling, or other symptoms of infection, see your dentist right away.
Treatment Options for Tooth Infections
- Antibiotics: If caught early, antibiotics can help to stop the infection from spreading.
- Root canal: This procedure removes the infected tissue inside the tooth and seals it to prevent further infection.
- Tooth extraction: If the tooth cannot be saved, it may need to be removed to stop the spread of infection.
- Surgical drainage: In some cases, the abscess may need to be drained to remove the pus and reduce pressure.
The Role of Dentistry in Preventing Life-Threatening Infections
Dentistry plays a vital role in preventing tooth infections from becoming fatal. Beyond cosmetic and routine care, dentists are trained to identify and treat infections before they cause serious harm. Regular dental visits are key to maintaining good oral health and preventing complications from tooth infections.
Pediatric Dentistry and Tooth Infections
Children are also at risk for tooth infections, especially if they experience tooth decay or trauma. Pediatric dentists can help ensure that children’s oral health is managed to avoid these serious complications. Untreated infections in children can have lifelong consequences, including the loss of teeth and health issues.
Dental Implants and Infection Risks
While dental implants are generally safe, infections can occur if proper care is not taken. Keeping the implant site clean and attending follow-up appointments with your dentist can prevent complications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How long until a tooth infection kills you?
If left untreated, a tooth infection could lead to life-threatening complications within weeks to months. In severe cases, death could occur in one to three days if the infection spreads quickly to the bloodstream or vital organs.
2. What are the symptoms of a severe tooth infection?
Symptoms include pain, swelling, fever, difficulty swallowing or breathing, and a bad taste in the mouth due to pus drainage. Severe infections may cause swelling of the face and neck, and in rare cases, difficulty breathing.
3. Can a tooth infection kill you?
Yes, in extreme cases, untreated tooth infections can spread to the bloodstream or vital organs, leading to sepsis, brain abscesses, or even death.
4. How do you treat a tooth abscess?
Tooth abscesses are treated by draining the abscess, taking antibiotics, performing a root canal, or extracting the infected tooth. Early intervention is crucial to prevent the infection from spreading.
5. How can I prevent a tooth infection?
To prevent a tooth infection, maintain good oral hygiene, visit your dentist regularly, and address any dental issues as soon as they arise.
Conclusion
Tooth infections are more than just a dental issue—they can pose serious threats to your overall health and even your life. Recognizing the symptoms early, seeking prompt treatment, and taking preventive measures can help you avoid the risks associated with untreated tooth abscesses. If you’re experiencing symptoms of a tooth infection, don’t wait—see a dentist before it’s too late.
 Skip to content
Skip to content

